Kaggle 的 Intro to Deep Learning 的笔记。
1. A Single Neuron
创建单个神经元
1 | from tensorflow import keras |
其中 layers.Dense() 表示一个稠密层,units 表示该层输出元素个数,input_shape=[height, width, channels] 描述该层输入大小。
用 model.weights 获取参数。
2. Deep Neural Networks
创建网络
1 | model = keras.Sequential([ |
也可以使用 layers.Activation('relu')。
其他激活函数
ReLU:
$$ReLU(x) = \max{0, x}$$
ELU:
$$
ELU(x, \alpha) =
\begin{cases}
x, &x \geq 0 \
\alpha(e^x - 1), &x < 0
\end{cases}
$$
SeLU:
$$
SeLU(x) =
\begin{cases}
\lambda_{selu}x, &x \geq 0 \
\lambda_{selu}\alpha_{selu}(e^x - 1), &x < 0 \
\end{cases}
$$
其中 $\alpha_{selu} \approx 1.6733, \lambda_{selu} \approx 1.0507$。
3. Stochastic Gradient Descent
- RMSE(Root Mean Square Error,均方根误差)
- MAE(Mean Absolute Error,平均绝对误差)
1 | # 钦定模型所用的 optimizer 和损失函数 |

4. Overfitting and Underfitting
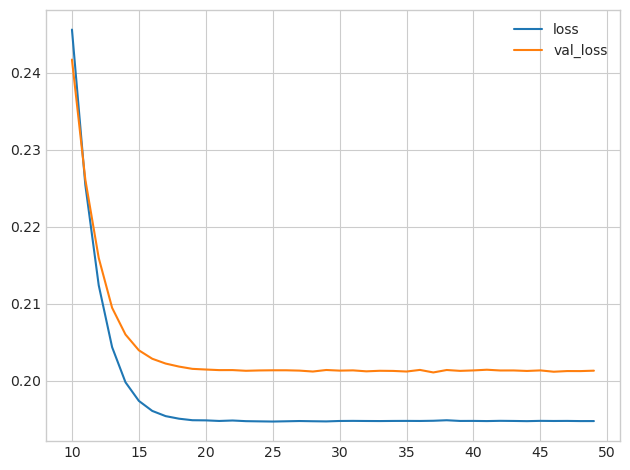
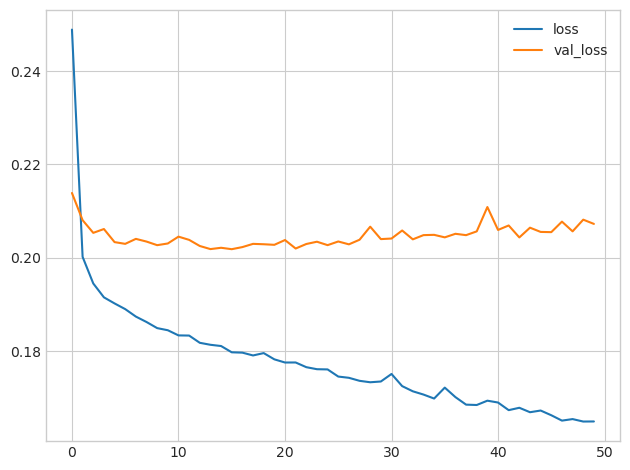
提前停止(Early stopping)
Keras 中,Early stopping 是一种回调(Callback)函数,每次迭代后都会执行。
1 | from tensorflow.keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping |
5. Dropout and Batch Normalization
Dropout
layers.Dropout(rate=0.3)
Batch Normalization(BN)
BN 层拥有两个可训练的参数 $\mu, \beta$。首先,BN 会对输入参数进行正则化($\mu = 0, \sigma = 1$),即 $x_i \leftarrow \frac {x_i - \mu}{\sqrt {\sigma^2 + \epsilon}}$;之后再让 $x_i \leftarrow \mu x_i + \beta$。这样可以在正则化数据的同时,又用 $\mu, \beta$ 作为还原参数,一定程度上保留原数据的分布。
BN 层一般可以缓解梯度爆炸或梯度消失的问题,也能使训练变得更快。
layers.BatchNormalization()
示例:
1 | model = keras.Sequential([ |
6. Binary Classification
Cross-Entropy(交叉熵)
分类问题使用的损失函数,即 $-\ln p_x$。
示例
1 | model = keras.Sequential([ |